Handling errors effectively is crucial in ensuring the stability and reliability of your React applications. In this article, we’ll explore various techniques for handling errors in React, accompanied by practical examples. By the end of this guide, you’ll have a comprehensive understanding of how to detect and manage errors in different scenarios within your React projects.
1. The Classic ‘Try and Catch’ Method in React
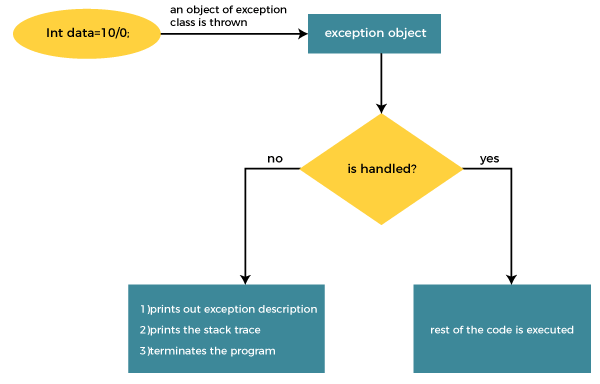
The traditional try and catch approach is a fundamental error handling technique that can be used in React as well. We’ll explore how to use it to gracefully handle errors within component code.
Try and Catch Example in React:
function ErrorExample() {
try {
// Code that may throw an error
const result = 10 / 0;
return <div>{result}</div>;
} catch (error) {
return <div>Error: {error.message}</div>;
}
}

2. React Error Boundaries
React Error Boundaries are components that catch JavaScript errors anywhere in their child component tree. We’ll learn how to create and use custom error boundaries to prevent errors from propagating to the entire application.
React Error Boundaries Example:
class ErrorBoundary extends React.Component {
state = { hasError: false };
static getDerivedStateFromError(error) {
return { hasError: true };
}
render() {
if (this.state.hasError) {
return <div>Something went wrong.</div>;
}
return this.props.children;
}
}
function App() {
return (
<ErrorBoundary>
{/* Your components */}
</ErrorBoundary>
);
}
3. Error Catching in Event Handlers
Events can trigger errors in React components. We’ll see how to wrap event handlers with error handling logic to prevent uncaught errors from breaking the application.
Error Catching in Event Handlers Example in React:
class EventHandlerExample extends React.Component {
handleClick = () => {
try {
// Code that may throw an error
const result = 10 / 0;
console.log(result);
} catch (error) {
console.error('Error:', error);
}
};
render() {
return <button onClick={this.handleClick}>Click me</button>;
}
}
4. Error Catching in setTimeout Calls
Errors within asynchronous operations like setTimeout can be challenging to catch. We’ll demonstrate how to wrap such operations with error handling logic.
Error Catching in setTimeout Calls Example in React:
class TimeoutExample extends React.Component {
componentDidMount() {
setTimeout(() => {
try {
// Code that may throw an error
const result = 10 / 0;
console.log(result);
} catch (error) {
console.error('Error:', error);
}
}, 1000);
}
render() {
return <div>Async operation example</div>;
}
}
5. JavaScript’s react-error-boundary Package
The react-error-boundary package provides an out-of-the-box solution for error boundaries in React. We’ll explore how to use this package to simplify error handling.
JavaScript’s react-error-boundary Package Example in React:
npm install react-error-boundary
import { ErrorBoundary } from 'react-error-boundary';
function App() {
return (
<ErrorBoundary
fallbackRender={({ error }) => <div>Error: {error.message}</div>}
>
{/* Your components */}
</ErrorBoundary>
);
}
6. Using Your Own React Boundaries
Creating your own custom error boundaries allows you to tailor error handling to your application’s specific needs. We’ll discuss strategies for implementing custom boundaries effectively.
Using Your Own React Boundaries Example:
class CustomErrorBoundary extends React.Component {
// Custom error handling logic
// ...
render() {
if (this.state.hasError) {
return <div>Custom error message</div>;
}
return this.props.children;
}
}
Conclusion
By mastering these error handling techniques in React, you’ll be better equipped to prevent errors from disrupting your application’s functionality and user experience. From the classic ‘try and catch’ method to leveraging powerful libraries like react-error-boundary, you’ll have a variety of tools at your disposal to create more robust and reliable React applications. Remember, effective error handling not only prevents crashes but also enhances the overall quality of your software.
Best Course To Learn React Js
– Name – React – The Complete Guide 2023 (incl. React Router & Redux)
– Rating – 4.6⁄5 (192,833 ratings)
– Students – 771,443
– Highlights – 50.5 hours on-demand video | 15 coding exercises | Assignments | 58 articles | Certificate of completion